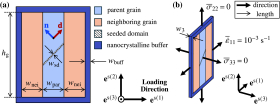
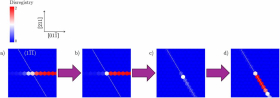
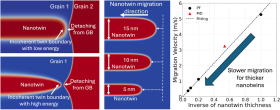
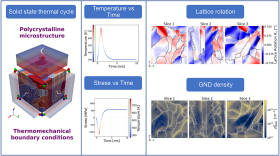
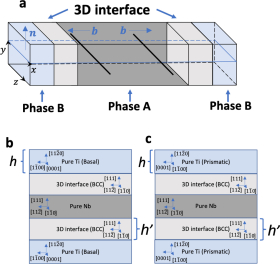
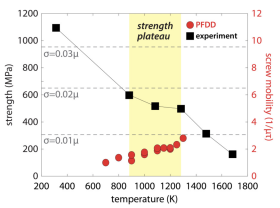
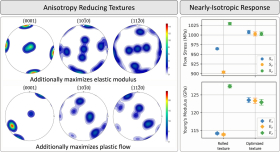
Postdoctoral researcher Yixi Shen and graduate student Ryan Leroux represented the Beyerlein group at the NSF ACCESS Regional AI Workshop – SoCal Edition, which brought together researchers, educators, and students from across Southern California to explore applications of AI and advanced computing in their work.